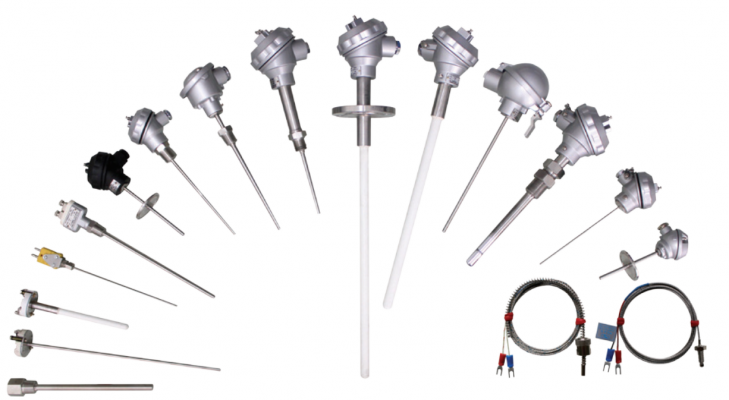
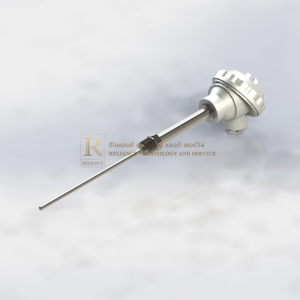
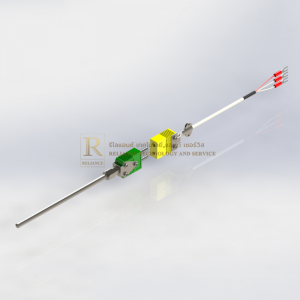
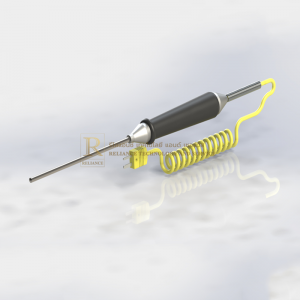
ผู้จัดจำหน่าย RTD คุณภาพสูง มาตรฐานสากล
RTD SENSORS
RTD แบ่งออกเป็น
-
-
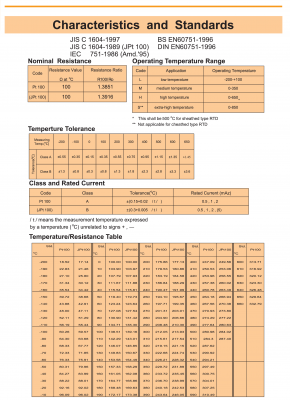
- ชนิด : PT100, PT1000 Class A, B, DIN1/10 (Single – 2,3,4 wires / Double -4,6 wire)
- ปลอกป้องกัน RTD : 1.6mm., 3.2mm., 4.8mm., 6mm., 6.4mm., 8mm (เดี่ยว/คู่)
- ท่อ : SS316L ขนาดเส้นผ่าศูนย์กลางท่อ : 3mm. – 16mm.
-
Applications
– Power & Utilities –Turbines / Bearing Temperature
-Oil & Gas application -Spares / replacement assembly
-Chemical & petrochemical -Pumps, compressors & diesel engines
-Water, waste-water treatment -Cement Industries
-Bearing temperature measurement -Air & flue gas applications
-Nuclear applications -Refinery & Petrochemicals Plants
-Autoclave applications -Stator winding of motors & generator
-Steel & Power applications –Pharmaceutical, Food & Beverages
-Surface measurement in refractoy vessels
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) Generally, electrical resistance of any metallic conductor varies according to temperature changes. The sensor for measurement of temperature by utilizing this phenomenon is called “Resistance Thermometer” or “RTD” and can measure temperature more precisely than other temperature sensors.
Its Features
Resistance Temperature Detectors for industrial applications have the following features.
1. Good sensitivity
2. Excellent stability and reproducibility
3. High accuracy
Structure and Measuring Methods
Structure:
Metal wire that changes its electric resistance to changes in temperature are utilized is called “Resistance Wire” This resistance wire, normally of platinum, is used to manufacture a temperature sensor called “Resistance
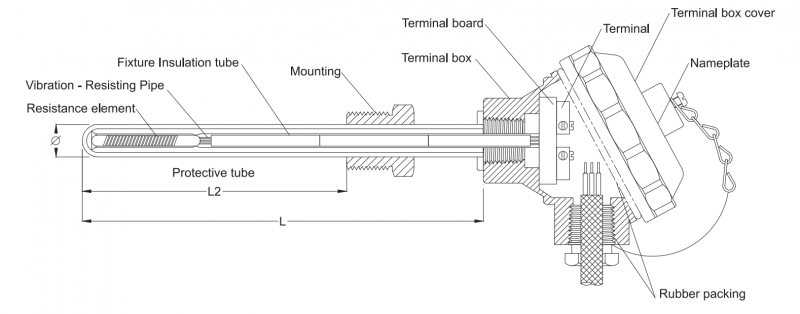
Temperature Detectors (RTDs)Element”.Generally speaking, RTD is composed of RTD element, lead wires, protection tube and terminals.
Measure Methods:
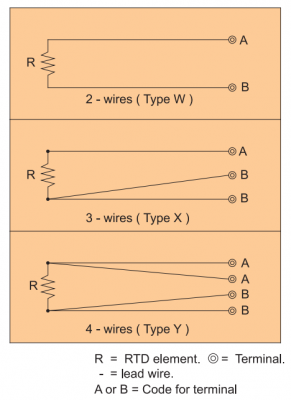
2-Wires Connection: Type W
RTD element is connected to respective two wire leads. Although it is less expensive than other types, it is not recommendable for high precision measurement of temperature because it is susceptible to lead resistance and produces error.
3-Wires Connection: Type X
One end of RTD element is connected to two wire leads and the other end connected to single lead to eliminate the effect from lead resistance. This type is most widely used as reliable method in industrial applications.
4-Wires Connection: Type Y
RTD element is connected to respective two wire leads to remove the effect from lead resistance. This connection cancels lead resistance effect and is especially recommendable for high precision measurement of temperature but somewhat expensive than other types.
RTD element is connected to respective two wire leads to remove the effect from lead resistance. This connection cancels lead resistance effect and is especially recommendable for high precision measurement of temperature but somewhat expensive than other types.
Precautions in practical Applications
Selection of proper RTD suitable for the application is the most important factor. For precision measurement of temperature, consideration should be given to selection of RTD element, protection tube, structure and fitting (location) according to the respective resistance to heat, corrosion, mechanical shock and other environmental conditions.
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
Construction
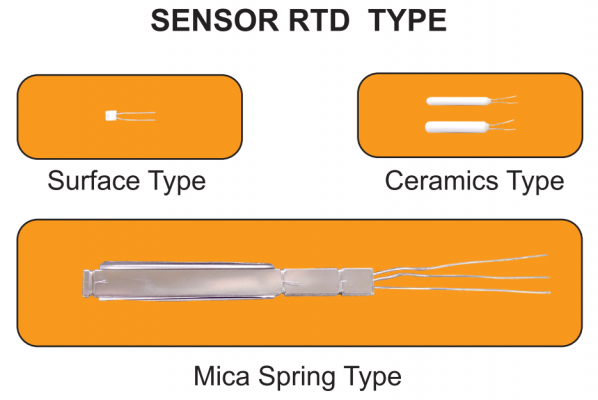
Temperature can be measured by utilizing a pure metal wire’s resistance, which increases at afixed rate with increasing temperature. Platinum resistance elements used most commonly for this purpose consist of a pure platinum resistance wire wound around a mica strip or other material. Some elements are formed by winding the resistance wire around a glass or mica core frame and sealing the assembly in a hard glass or ceramic tube. The element is attached with lead wires (two or three) and put in a protecting tube, with a terminal box and mounting fittings connected.
RTDs
RTD RTS1
RTDs
RTD RTS2
RTDs
RTD RTS3
RTDs
RTD RTS4
RTDs
RTD RTS5
RTDs
RTD RTS6
RTDs
RTD RTS7
RTDs
RTD RTS8
RTDs
RTD RTS9
RTDs
RTD RTS10
RTDs
RTD RTS11
RTDs
RTD RTS12
RTDs
RTD RTS13
RTDs
RTD RTS14
RTDs
RTD RTS15
RTDs
RTD RTS16
RTDs
RTD RTS17
RTDs
RTD RTS18
RTDs
RTD RTS19
RTDs
RTD RTS20
RTDs
RTD RTS21
RTDs
RTD RTS22
RTDs
RTD RTS23
RTDs
RTD RTS24
RTDs
RTD RTS25
RTDs
RTD RTS26
RTDs
RTD RTS27
RTDs
RTD RTS28
RTDs
RTD RTS29
RTDs
RTD RTS30
RTDs
RTD RTS31
RTDs
RTD RTS33
RTDs
RTD RTS34
RTDs
RTD RTS35
RTDs
THERMOWELL RTS-TW1
RTDs
THERMOWELL RTS-TW2
RTDs
THERMOWELL RTS-TW3
RTDs
THERMOWELL RTS-TW4
RTDs
THERMOWELL RTS-TW5
RTDs